CSS Flexbox Cards | Creating a Modern CSS Card Design Layout
12/10/2020
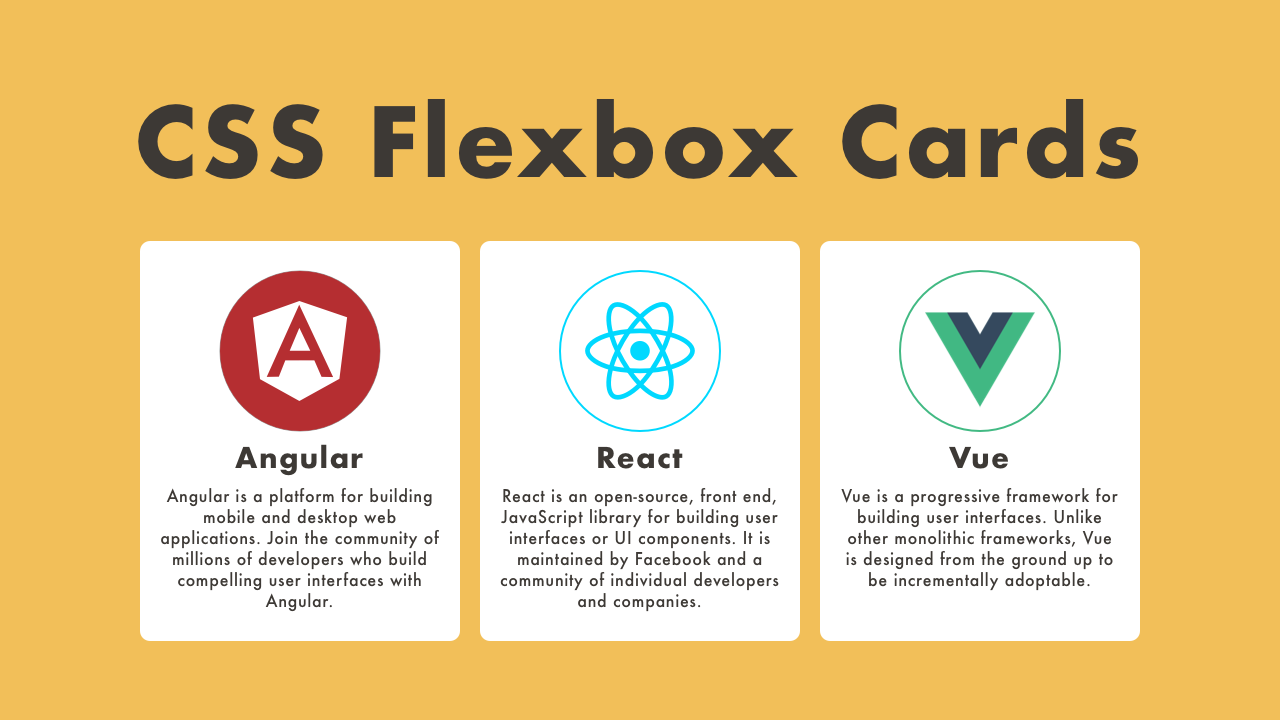
Demo
Code
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1">
<title>CSS Flexbox Cards</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="https://demo.plantpot.works/assets/css/normalize.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://use.typekit.net/opg3wle.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="style.css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="container">
<div class="box">
<h1>CSS Flexbox Cards</h1>
<div class="cards">
<article class="card">
<a href="#">
<figure class="card-thumb">
<img src="angular.png" alt="angular">
</figure>
<div class="card-content">
<h2 class="card-title">Angular</h2>
<p class="card-excerpt">Angular is a platform for building mobile and desktop web applications. Join the community of millions of developers who build compelling user interfaces with Angular.</p>
</div>
</a>
</article>
<article class="card">
<a href="#">
<figure class="card-thumb">
<img src="react.png" alt="react">
</figure>
<div class="card-content">
<h2 class="card-title">React</h2>
<p class="card-excerpt">React is an open-source, front end, JavaScript library for building user interfaces or UI components. It is maintained by Facebook and a community of individual developers and companies.</p>
</div>
</a>
</article>
<article class="card">
<a href="#">
<figure class="card-thumb">
<img src="vue.png" alt="vue">
</figure>
<div class="card-content">
<h2 class="card-title">Vue</h2>
<p class="card-excerpt">Vue is a progressive framework for building user interfaces. Unlike other monolithic frameworks, Vue is designed from the ground up to be incrementally adoptable.</p>
</div>
</a>
</article>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS
@charset "utf-8";
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
html {
font-size: 16px;
}
body {
background-color: #f2bf59;
color: #3d3935;
font-family: futura-pt, sans-serif;
-webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(0,0,0,0);
}
#container {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
width: 100%;
height: 100vh;
}
.box {
width: 100%;
max-width: 600px;
padding: 15px;
}
.box h1 {
margin: 10px 0;
color: inherit;
font-size: 2.5rem;
letter-spacing: 2px;
text-align: center;
}
.cards {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
justify-content: space-between;
width: 100%;
}
.card {
width: 32%;
padding: 15px 10px;
background-color: #fff;
border-radius: 3px;
transition: transform .3s;
}
.card a {
color: inherit;
text-decoration: none;
}
.card-thumb {
width: 100%;
text-align: center;
}
.card-thumb img {
width: 80px;
}
.card-title {
margin: 5px 0;
font-size: 1.25rem;
letter-spacing: 1px;
text-align: center;
}
.card-excerpt {
font-size: .75rem;
letter-spacing: 1px;
text-align: center;
}
.card:hover {
box-shadow: 0px 0px 20px -5px rgba(0, 0, 0, .2);
transform: translateY(-4px);
}
@media screen and (max-width: 540px) {
#container {
height: auto;
}
.box {
padding: 20px;
}
.card {
width: 49%;
}
}
@media screen and (max-width: 480px) {
.box h1 {
font-size: 1.5rem
}
.cards {
justify-content: center;
}
.card {
margin-bottom: 20px;
width: 80%;
}
}